What is Pain?
The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), which is the world’s largest pain-related professional organization, revised their official definition of pain last year. It reads: “Pain is a sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage.” It was a revision of their earlier version from 1979, which also contained the phrase defining pain as a “sensory and emotional experience.”
This definition of pain is arguably accepted worldwide by clinicians, researchers, and policy-makers.
It is also commonly surprising to patients. For who thinks of pain as even in part emotional?
After all, pain is a sensation, not an emotion. Pain is like itches, tickles, numbness and tingling. All these experiences are sensations. They are associated with our tactile sense of perception. We do not see, hear or taste pain and itches and the like, but rather we tactilely feel them. Emotions are experiences such as being happy or mad or sad or joyful. These experiences are rightly not considered sensations.
There is, however, cross over between the experiences of sensations and emotions. It is readily apparent with emotions, which commonly involves also having sensations. Excitement and fear, for instance, are palpable. We can sometimes almost burst with tingling energy when excited. Grade school children have tummy aches the night before the first day of school. Less readily acknowledged is that sensations also have emotional aspects to them.
Itches are aggravating, especially when they don’t easily go away, and scratching them is relieving. Tickles make us giggle, and we squirm in their playfulness.

Pain is alarming. We wince, guard and protect. We cry tears and we cry out verbally. We look to others for help, and others react accordingly. Pain is a sensation that alerts us to something that is going wrong. It puts us on notice.
In this way, pain is like a fire alarm in a building. Fire alarms alert us to something that is going wrong in the building and we reflexively react with avoidance behaviors — we get out of the building. In a word, fire alarms are alarming. They are an auditory perception that is inherently alarming.
Pain is a similarly alarming perception. Of course, we do not hear pain, but feel it. We perceive it through our tactile sense, but it involves a similarly alerting and cautionary experience to which we reflexively react with avoidant behaviors (e.g., reflexively pulling away our hand from flame).
We thus might capture the definition of pain as “a sensory and emotional experience” with a quasi-equation: pain = sensation + alarm.
Mapping Pain onto the Brain
Pain as a sensory and emotional experience maps onto the brain. Suppose you broke your ankle, or stepped on a nail, or some other typically painful injury, and further suppose you were put into an MRI for a brain scan. Different parts of the brain that roughly correspond to both the felt sensation and alarm would light up in the scan (Da Silva & Seminowicz, 2019; Sperry et al., 2017).
First, the somatosensory cortex of the brain would show up as active. This area of the brain corresponds to the sensation that would be felt. It is largely responsible for the type of sensation (whether it would be a dull ache, a sharp piercing sensation, an electrical sensation, or what have you) and where in the body it will be felt (the left ankle that has the fracture or the right foot with the nail sticking in it). Second, in addition to the somatosensory cortex, the scan would reveal activity in the limbic system and prefrontal cortex. These areas are responsible for a great many things, but one of which is our danger response, commonly known as “fight-or-flight” or “fight, flight, or freeze.” It is our innate alarm system — something that gets activated in response to threat.
It makes sense that we’d be built this way — that our danger response would go off when having a certain sensation that we call pain. It is signaling danger in the sense of harm. We accidentally touch flame with our hand or we break our ankle or step on a nail. Something is going wrong and as a result we experience pain.
Pain is the only sensation that puts us on notice in this way. It alerts us and we reflexively guard, protect, pull away and seek help. No other sensation, such as tickles or itches or numbness, typically puts us into a state of alarm. In this way, pain is an inherently alarming sensation.
In our effort to clarify the IASP definition of pain as a ‘sensory and emotional experience… associated with… tissue damage,” we can thus be even more specific: pain is a sensation with an innate sense of alarm, or a sensory and alarming experience.
More information
For more information, please see these related topics: the neuromatrix of pain, central sensitization, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and the mission of the Institute for Chronic Pain to educate the public about empirical-based conceptualizations of pain and its treatments.
References
Da Silva, J. T. & Seminowicz, D. A. (2019). Neuroimaging of pain in animal models: A review of recent literature. Pain, 4(4), e732. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000732
Sperry, M. M., Kandel, B. M., Wehrli, S., Bass, K. N., Das, S. R., Dhillion, P. S., Gee, J. C., & Bar, G. A. (2017). Mapping of pain circuitry in early post-natal development using manganese-enhanced MRI in rats. Neuroscience, 352, 180-189. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.03.052
Date of initital publication: October 11, 2021
Date of last modification: October 11, 2021
Fatigue and Chronic Pain
Fatigue associated with chronic pain
Daytime fatigue1 is commonly reported with chronic pain and can be just as challenging to manage.2 Restorative sleep is undoubtedly important and adhering to the guidelines for sleep restriction and sleep hygiene can improve the quality and often the quantity of sleep. Less well-known are diurnal rhythms, which are independent daytime biological patterns, and how they affect us and how we can affect them. Changing what we do, how and when we do them, can help these invisible hormonal and chemical patterns synchronize and as a result have less fatigue.
What is the Neuromatrix of Pain?
The notion of a neuromatrix of the brain is a theoretical model that explains the nature of pain, including chronic pain. Ronald Melzack, PhD, a psychologist, and one of the founding fathers of the field of pain management as we know it today, developed the theory and published it in a series of papers at the end of the last century.1, 2, 3, 4 Melzack had previously revolutionized the field of pain management in an earlier theory that he had developed and published with his physician colleague, Patrick Wall, in what is known as the gate control theory of pain.5 Few theories in modern science have spawned more empirical research than those of the gate control theory of pain and the neuromatrix of pain. Indeed, while technically theories, the field largely considers these models as accurate explanations of the nature of pain, given the great wealth of empirical evidence that now confirms them. So, what is this notion of the neuromatrix of the brain that explains the nature of pain?
How to End the Stigma of Pain
Stigma is a significant and persistent problem for those with chronic pain. Stigma occurs when someone is judged for having a condition that they didn't choose to have, like chronic pain. In other words, stigma is the criticism of being bad in some way for simply having a condition that you didn't choose to have. It can also occur in relationship to how a patient with chronic pain is coping. Stigma thus arises when moral judgments occur not for wrong behavior, which might rightly get criticized, but for simply being who you are, for simply having the health condition that you have, or for how you are dealing with it.
Insomnia
What is insomnia?
Insomnia is a sleep problem that is marked by having difficulty falling asleep at the beginning of the night or returning to sleep upon awakening in the middle of the night.
Insomnia is common in persons with chronic pain. Upwards of half of all people with chronic low back pain, for instance, report insomnia.1, 2
On the Meaning of "Chronic"
The meaning of "chronic" and why the healthcare system refuses to accept the chronicity of chronic pain
We live in an age of chronic illness. Conditions like heart disease, diabetes, asthma and chronic pain are common. All these health conditions are chronic. The term chronic means that a condition has no cure and so will last indefinitely.
Healthcare System Failings
It’s common to complain about healthcare and our healthcare system. We complain about our health insurance and we also complain about reforms to the health insurance industry. We complain about the long wait times to see a provider. We also complain about the short amount of time that we actually get once we see a provider. We complain about how much money we pay for healthcare. We also complain about how much money certain providers and insurance executives get paid. With our healthcare system so large and complex, most anyone can find something to complain about.
Opioid Dependance and Addiction
Opioid, or narcotic, pain medications are beneficial in a number of ways. Terminal cancer patients, for instance, benefit from their use. The short-term use of opioid pain medications is beneficial, especially while recovering from an acute injury or a surgery. However, the long-term use of opioid medications for chronic, noncancer, pain remains controversial. While a number of issues contribute to this controversy, the main reason for the controversy is addiction. Opioid pain medications are addictive.
This controversy makes opioid pain medications a highly sensitive issue for patients who take them.
Sleep Disturbance
What is a sleep disturbance?
Patients with chronic pain frequently experience sleep disturbances. Sleep disturbance is a catchall phrase for any type of problem in sleeping. The most common forms of sleep disturbances in patients with chronic pain are the following:
Depression
What is depression?
From time to time, most people feel down, blue, unhappy, or irritable. These kinds of depressed moods come and go in response to the normal problems of life.
Anxiety
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a normal emotion. Everyone has anxiety on occasion. It is the emotion that people have when something dangerous might happen. Anxiety is closely related to fear. Fear occurs when something dangerous is happening. Anxiety, though, occurs when something dangerous is pending, and hasn’t happened yet, though it could.
Complications
What are complications to pain?
A number of problems are associated with living with chronic pain.
Social Stigma
What is stigma?
Stigma is the social disapproval of a characteristic of a person and, typically, the characteristic is not changeable or not easily changeable. The disapproval is a critical judgment that an individual is not normal and has less worth than those in the norm. A natural response to stigma is shame and shame-based defensive anger.
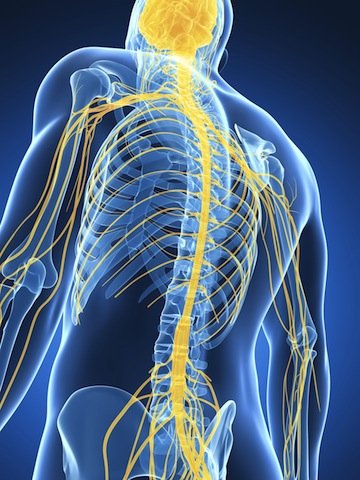
What is Central Sensitization?
Central sensitization is a condition of the nervous system that is associated with the development and maintenance of chronic pain. When central sensitization occurs, the nervous system goes through a process called wind-up and gets regulated in a persistent state of high reactivity. This persistent, or regulated, state of reactivity lowers the threshold for what causes pain and subsequently comes to maintain pain even after the initial injury might have healed.
Chronic Pain Syndrome
What is a chronic pain syndrome?
Your doctor has told you that you have a chronic pain syndrome. What does it mean?
In most cases, chronic pain starts with an acute injury or illness. If the pain of this injury or illness lasts longer than six months, it’s then considered chronic pain. Sometimes, chronic pain subsequently causes complications. These complications, in turn, can make the pain worse. A chronic pain syndrome is the combination of chronic pain and the secondary complications that are making the original pain worse.
What is Chronic Pain?
Patients and healthcare providers commonly think of pain as a symptom of an underlying injury or illness. Say, for example, you hurt your low back while lifting. Perhaps, you’ve injured a muscle or ligament, or perhaps it’s an injury to the spine, like a disc bulge or herniation. Either way, you now have pain and the pain is the symptom of the injury. The same might be true for any health condition that causes pain, particularly when it first starts.
